

Updated: 2024-10-12
Freeform optics is considered one of the representative cutting-edge technologies in the field of optical engineering. One of its core functions is to control the light energy distribution of the light source, thereby forming any desired light energy distribution pattern on the target surface. This technology plays an important role in many critical areas such as automotive lighting and machine vision illumination. However, effectively constructing compact freeform structures for extended light source forms that do not satisfy the point source approximation remains a major challenge in current research.
Associate Professor Feng Zexin from the School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), and his doctoral students Tang Haisong and Li Haoran, in collaboration with Academician Luo Yi from the Department of Electronic Engineering at Tsinghua University and Researcher Mao Xianglong from the Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have proposed a multi-scale design method for a double-freeform lens based on differentiable ray tracing.
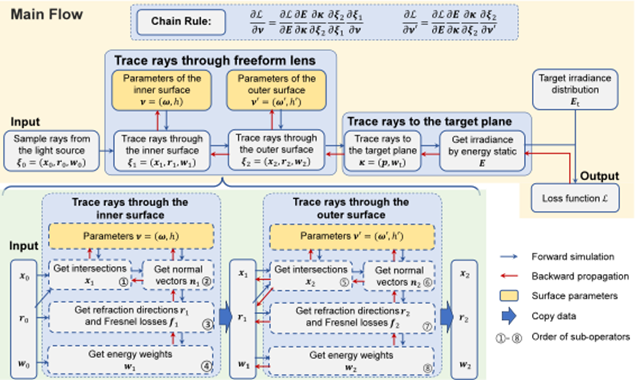
Freeform surface differential ray tracing simulation framework
This method provides a flexible, universal, and efficient design solution for the challenging task of tailoring irradiance for extended light sources. Their related work has been published under the title Differentiable design of a double-freeform lens with multi-level radial basis functions for extended source irradiance tailoring in the Optica, a top international journal in the field of optics.
This research utilizes SRBFs to characterize freeform surfaces, achieving fine control from global to local by progressively adding SRBF terms. With this representation and by targeting an expanded light source model, the study employs computational graph techniques to construct a differentiable ray tracing simulation framework. It adopts a multi-scale optimization strategy that matches the multi-layer representation, incrementally enhancing spot accuracy while effectively reducing reliance on initial solutions, thereby boosting design efficiency.
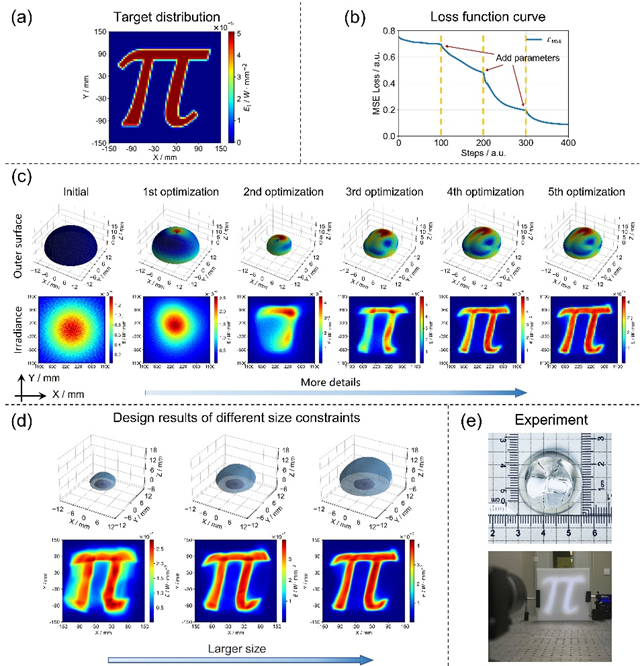
Design and experimental verification of freeform surface lenses
This method has high design efficiency, low dependence on the initial structure in the design process, and high light utilization efficiency of the designed lens. Not only can it achieve complex irradiance distribution forms, but also balance between lens size and control effects. This research has extremely high application value in the fields of semiconductor light source integration, new energy vehicle headlights, and automatic inspection lighting.
Paper details: Tang Haisong, Li Haoran, Feng Zexin, Luo Yi, Mao Xianglong. Differentiable design of a double-freeform lens with multi-level radial basis functions for extended source irradiance tailoring [J]. Optica, 2024, 11(5): 653-664. DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.520485














